When it comes to taxes, two forms that often cause confusion are the W-9 and the W-4. While they may seem similar, they serve very different purposes. This article will break down the key differences between these two common tax forms.
What is a W-4?
The W-4 form, officially titled “Employee’s Withholding Certificate,” is used by employees to inform their employer how much federal income tax to withhold from their paycheck. This form takes into account factors like:
- Filing status: (Single, Married, Head of Household, etc.)
- Number of dependents:
- Multiple jobs:
- Other income:
- Deductions:
By accurately completing a W-4, employees can ensure that the correct amount of tax is withheld from their earnings, avoiding a large tax bill or a significant refund at the end of the year.
What is a W-9?
The W-9 form, officially titled “Request for Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) and Certification,” is used by independent contractors, freelancers, and other non-employees to provide their Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) to the entities that pay them. This form is used to report payments made to these individuals to the IRS. The W-9 Form includes:
- Name:
- Business name/disregarded entity name:
- Tax classification: (Individual/sole proprietor, C-Corp, S-Corp, Partnership, etc.)
- TIN: (Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN))
- The information on the W-9 allows payers to accurately file information returns, such as Form 1099-NEC, with the IRS.
Key Differences: W-9 vs. W-4
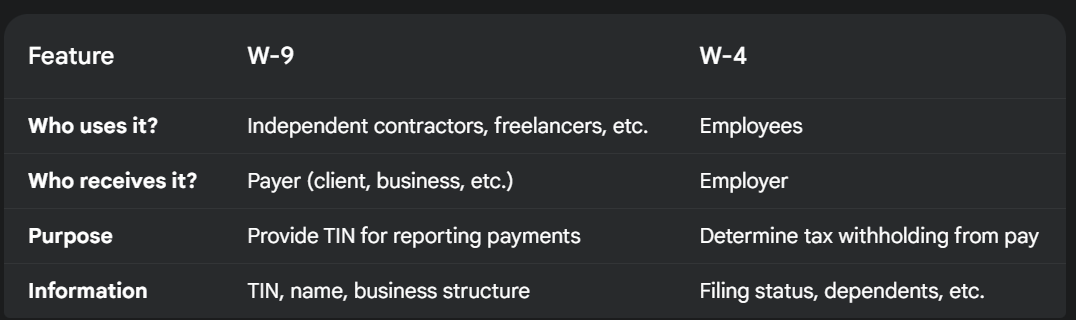
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between the W-9 and W-4:
In Simple Terms
- W-4: Tells your employer how much tax to take out of your paycheck.
- W-9: Tells the person paying you (not your employer) your tax information so they can report how much they paid you to the IRS.
Understanding the difference between these two forms is crucial for both individuals and businesses to ensure accurate tax reporting and compliance.
Understanding the difference between these two forms is crucial for both individuals and businesses to ensure accurate tax reporting and compliance.